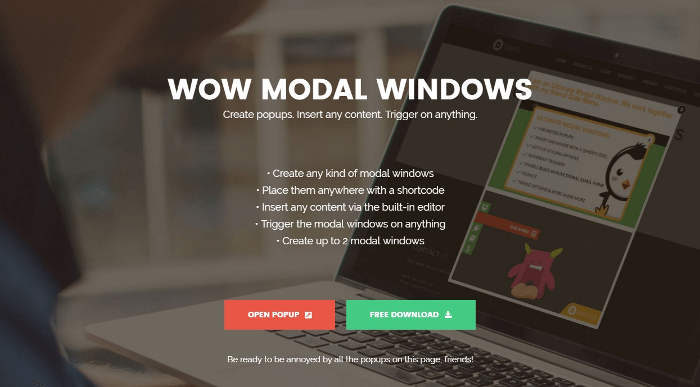
Understanding Modal Windows’ Role in User Interaction
Modal windows, when designed thoughtfully, serve as effective tools to convey important information or guide users toward specific actions without redirecting from the current context. Before diving into the design intricacies, it’s crucial to understand their purpose within the broader user experience framework.

Principles of Seamless Modal Window Design
1. Simplicity and Clarity
Ensure a clean and uncluttered design. Use minimalistic visuals and clear, concise content to communicate the intended message or action.
2. Consistency with Branding
Maintain consistency with your website’s overall design and branding elements. Colors, fonts, and visual cues should align with the site’s aesthetics.
3. Responsiveness
Prioritize responsiveness across devices. Modal windows should adapt flawlessly to various screen sizes without sacrificing functionality or design.
4. Ease of Closure
Provide an easily identifiable and intuitive way to close the modal window. Users should have a clear path to return to their previous task or content.
User-Centric Modal Window Design Strategies
1. Contextual Relevance
Display modal windows at appropriate moments in the user journey, offering relevant information or actions based on user behavior or interaction.
2. Progressive Disclosure
Use modal windows to gradually disclose information. Start with essential details and allow users to delve deeper if they choose.
3. Visual Hierarchy
Emphasize key elements within the modal window using visual hierarchy. Direct attention to the primary message or call-to-action using size, color, or placement.
Interaction and Functionality
1. Gentle Animations
Incorporate subtle animations to improve user experience. Animations can guide attention and provide visual cues, enhancing the overall interaction.
2. Focus on Accessibility
Ensure modal windows are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. Use appropriate contrast, keyboard navigation, and screen reader compatibility.
Testing and Iterative Improvements
1. User Testing
Conduct user testing to gather feedback on the modal window design. Understand user preferences and pain points to refine the user experience.
2. A/B Testing
Experiment with variations of the modal window design. Test different layouts, content, or triggers to identify the most effective approach.
Analytics and Optimization
1. Track User Engagement
Implement analytics to track user interactions with modal windows. Monitor metrics such as conversion rates, time spent, and bounce rates.
2. Iterate Based on Data
Analyze the gathered data and iterate on the modal window design. Implement changes based on insights to continuously improve performance.
Conclusion
Designing seamless modal windows that enhance user interaction demands a blend of user-centricity, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. By adhering to design principles, considering user needs, and employing iterative improvements based on data-driven insights, you can create modal windows that not only seamlessly integrate into the user experience but also elevate engagement and interaction on your website.