The Power of Windows Event Viewer. errors and glitches are inevitable. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or an everyday user, encountering issues with your Windows system can be frustrating. Fortunately, Windows Event Viewer is a powerful tool that can provide valuable insights into system events and errors, aiding in troubleshooting and resolving issues efficiently. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore how the Windows Event Viewer works and how it can be leveraged to diagnose and troubleshoot various errors.The Power of Windows Event Viewer.
The Power of Windows Event Viewer
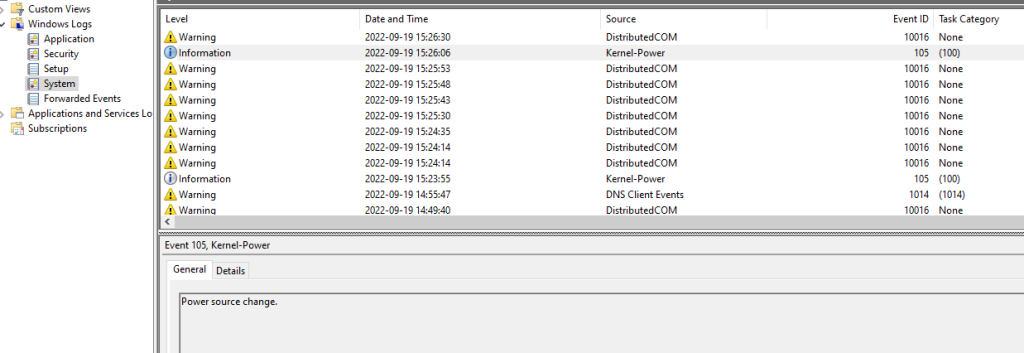
Understanding Windows Event Viewer: Windows Event Viewer is a built-in tool in Microsoft Windows operating systems that allows users to view and analyze system event logs. These logs contain information about application, security, and system events, providing a detailed record of activities and errors occurring on the system. Event Viewer categorizes events into different log types, including Application, Security, Setup, System, and Forwarded Events, making it easier to locate and analyze specific types of events.
How Windows Event Viewer Works
When an event occurs on a Windows system, such as a program crash or a system error, it is logged in the Event Viewer database. Each event is assigned a unique Event ID, which categorizes the event based on its type and severity. Additionally, events are timestamped, allowing users to track when they occurred. Windows Event Viewer provides a user-friendly interface for browsing and filtering event logs, making it easy to identify patterns and trends in system behavior.
Benefits of Using Windows Event Viewer for Troubleshooting: Windows Event Viewer offers several benefits that make it an indispensable tool for troubleshooting errors:
- Comprehensive Event Logging: Event Viewer logs a wide range of system events, including application crashes, driver failures, and system errors, providing a comprehensive overview of system activity.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Event Viewer allows users to monitor system events in real-time, enabling prompt detection and resolution of issues as they occur.The Power of Windows Event Viewer.
- Detailed Event Information: Each event logged in Event Viewer includes detailed information such as Event ID, Source, Description, and Error Codes, facilitating accurate diagnosis and troubleshooting.
- Customizable Filtering and Searching: Event Viewer offers powerful filtering and searching capabilities, allowing users to narrow down event logs based on criteria such as Event Type, Date and Time, Event ID, and Source.The Power of Windows Event Viewer.
- Centralized Event Management: In networked environments, Event Viewer can be configured to collect event logs from multiple computers, providing centralized event management and analysis capabilities.
How to Use Windows Event Viewer for Troubleshooting: To effectively leverage Windows Event Viewer for troubleshooting errors, follow these steps
- Open Event Viewer: Press Win + R to open the Run dialog, type “eventvwr.msc”, and press Enter to launch Event Viewer.
- Navigate Event Logs: In the Event Viewer window, navigate to the desired event log (e.g., Application, System) from the left-hand pane.
- Review Event Details: Select an event from the list to view its details, including Event ID, Source, Description, and Error Codes. Pay attention to any recurring patterns or trends.
- Filter Event Logs: Use the Filter Current Log option to filter event logs based on specific criteria such as Event Type, Date and Time, Event ID, and Source.
- Analyze Error Messages: Pay close attention to error messages and codes provided in event descriptions, as they often contain valuable clues about the underlying issue.
- Take Corrective Actions: Based on the information gathered from Event Viewer, take appropriate corrective actions to resolve identified issues, such as updating drivers, reinstalling software, or performing system repairs.
- Monitor for Resolution: After implementing corrective actions, monitor Event Viewer for any recurrence of the issue. If the problem persists, continue troubleshooting or seek further assistance.
- Event Categories: Windows Event Viewer categorizes events into different log types, each serving a specific purpose. Understanding these categories, such as Application, Security, Setup, and System logs, helps users navigate and focus on relevant events.
- Event Severity Levels: Events in Event Viewer are assigned severity levels such as Information, Warning, and Error. Understanding these severity levels helps prioritize troubleshooting efforts based on the criticality of the issue.
- Event Details: Each event logged in Event Viewer contains detailed information such as Event ID, Source, Description, and Error Codes. Learning how to interpret these details provides insights into the nature and cause of the error.
- Event Viewer Filters: Event Viewer offers powerful filtering capabilities to narrow down event logs based on specific criteria. Learning how to apply filters effectively helps focus on relevant events and reduce noise in the logs.
- Event Viewer Views: Event Viewer provides different views, such as Summary, List, and Details views, to display event information. Understanding how to switch between these views and customize the display enhances the usability of Event Viewer.
- Event Viewer Custom Views: Users can create custom views in Event Viewer to filter and display events based on user-defined criteria. Learning how to create and manage custom views allows users to tailor Event Viewer to their specific troubleshooting needs.
- Event Viewer Event Forwarding: In networked environments, Event Viewer supports event forwarding, allowing events from multiple computers to be collected and viewed centrally. Understanding how to configure event forwarding facilitates centralized event management and analysis.
- Event Viewer Event Properties: Each event in Event Viewer has properties such as Event ID, Task Category, and Keywords, which provide additional context about the event. Learning how to access and interpret these properties enriches the understanding of event details.
- Event Viewer Event Logs Backup: Regularly backing up Event Viewer event logs helps preserve historical event data for future reference and analysis. Understanding how to perform event logs backup ensures data integrity and continuity of troubleshooting efforts.